Comparative Analysis of DC Transmission and AC Power
Ⅰ.Introduction
When it comes to power delivery, AC and DC are the two common methods. DC transmission and AC transmission each have their own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of DC and AC transmission and compare their differences. This will help you understand the characteristics of these two technologies and their applications.
Ⅱ.DC transmission
2.1. Definition of DC transmission
DC transmission is a power transmission method that transmits electrical energy from power stations to loads in the form of direct current. In contrast, AC transmission is another common power transmission method, which transmits electrical energy from the power station to the load in the form of alternating current.
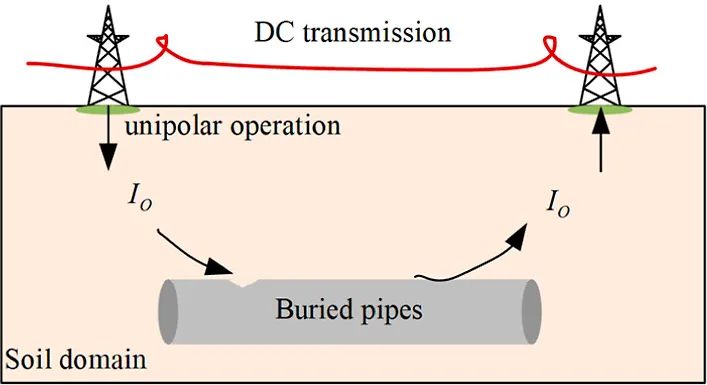
Figure1:DC transmission
2.2.Advantages of DC transmission
DC transmission is not restricted by synchronous operation stability issues and plays a great role in ensuring the stable operation of the AC power grid at both ends.
The DC transmission control system has fast response, precise adjustment, easy operation, and can achieve multi-objective control.
The voltage distribution along the DC transmission line is stable, there is no capacitive current, and no parallel reactance compensation is required.
Direct current transmission at both ends facilitates graded and phased construction and capacity expansion, which is conducive to early benefits.
2.3.Disadvantages of DC transmission
The converter consumes a lot of reactive power when working.
The overload energy of thyristor components is low.
When DC power transmission uses the earth or seawater as a return circuit, it will cause corrosion to metal facilities on the ground, underground or in seawater along the way. It will also cause interference to communications and navigation.
DC current does not have the zero-crossing point of the current waveform like AC current, so arc extinguishing is more difficult.
Ⅲ.AC power transmission
3.1.Definition of AC transmission
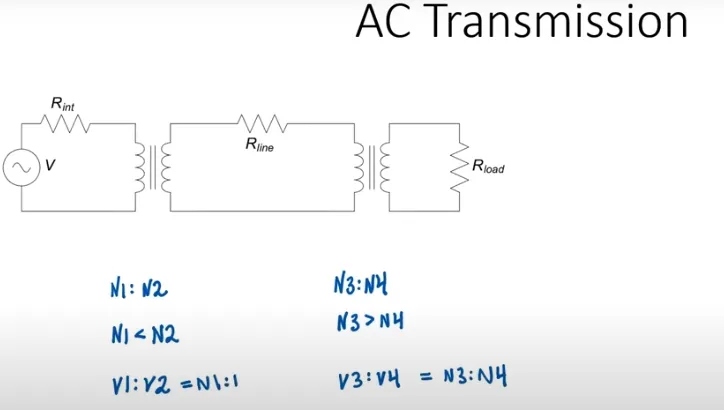
Figure2:.AC power transmission
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and continuously changes its magnitude over time, unlike direct current (DC) which flows in only one direction. Alternating current transmission is a method of transmitting electrical energy from one location to another using alternating current. It is a mature technology with low equipment costs and relatively low maintenance costs. 2. AC transmission systems can use transformers to step up or step down voltage, making it easier to transmit power over long distances. 1. However, AC systems may develop harmonic problems 2. and require compensating measures to resolve them.
3.2.Advantages of AC power transmission
AC transmission technology is mature, equipment costs are low, and maintenance costs are relatively low.
Transformers in AC systems can realize voltage step-up and step-down to facilitate long-distance transmission.
In AC systems, parallel connection can be used to improve transmission capacity.
3.3.Disadvantages of AC power transmission
There are harmonic problems in AC systems and some measures need to be taken to compensate.
There are inductive and capacitive loads in the AC system, and some measures need to be taken to compensate.
There is a short circuit problem in the AC system and some measures need to be taken to protect it.
Ⅳ.What are the advantages of DC power transmission over AC power?
DC transmission has several advantages over AC, including:
Lower power loss: Compared with AC, DC transmission has lower power loss, especially when transmitting over long distances. This is because DC power cords do not have reactive power losses like AC power cords.
Higher efficiency: DC transmission is more efficient than AC transmission. This is because DC power lines can transmit more power over the same distance with less energy loss.
Better voltage regulation: DC transmission allows for better voltage regulation compared to AC power. This is because DC power lines do not experience voltage drops due to reactive power losses.
Lower electromagnetic interference: Compared with AC power supply, DC transmission produces less electromagnetic interference. This is because DC power cords do not produce electromagnetic fields that can interfere with other electronic devices.
Suitable for renewable energy sources: DC transmission is well suited for transmitting electricity from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind energy. This is because these power supplies produce direct current that can be transmitted over long distances more efficiently.
Ⅵ.What are the applications of DC transmission and AC power?
DC transmission and AC power have different applications based on their unique characteristics. Here are some common applications for both:
Applications of DC Transmission:
Electric Vehicles: DC power is commonly used for charging electric vehicles due to its compatibility with batteries.
Renewable Energy Systems: DC transmission is used in solar power systems and wind turbines to convert and transmit the generated power.
Data Centers: DC power is used in data centers to improve energy efficiency and reduce power losses.
Submarine Cables: DC transmission is preferred for long-distance submarine cables due to its lower losses compared to AC transmission.
High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Systems: HVDC systems are used to transmit large amounts of power over long distances, such as interconnecting power grids.
Applications of AC Power:
Residential and Commercial Power Distribution: AC power is used for general power distribution in homes, offices, and commercial buildings.
Industrial Applications: AC power is widely used in industrial machinery, motors, and equipment.
Electric Grids: AC power is used for transmitting and distributing electricity in power grids, as it can be easily stepped
Heating, Vent
Appliances and Electronics: Most household appliances and electronic devices are designed to run on AC power.
It's important to note that the choice between DC transmission and AC power depends on various factors such as efficiency, cost, distance, and the specific requirements of the application.
Ⅶ.In conclusion
In general, DC transmission and AC transmission each have their own advantages and disadvantages. DC transmission has the advantages of fast response, precise adjustment, and easy operation, but it consumes more reactive power and may cause corrosion and interference to the surrounding environment. AC transmission technology is mature, the equipment cost is low, and maintenance costs are relatively low, but there are disadvantages such as harmonic problems and inductive and capacitive loads. In practical applications, the appropriate power transmission method should be selected according to specific conditions.
Ⅷ.FAQ
01What is the difference between DC transmission and AC power?
The main difference between DC and AC power is the direction of the current. In DC power, the current flows in one direction, whereas in AC power, the current changes direction periodically.
02Why is DC transmission more efficient than AC?
DC power is more efficient because, unlike AC power, it consists entirely of active power, resulting in minimal losses due to the capacitance of wires over long distances. High voltage AC transmission systems, on the other hand, experience losses of 7% to 15% with aboveground transmission.
03Why is AC used to transmit power instead of DC?
AC is preferred for power transmission because it is much easier and cheaper to step up and down in voltage using a transformer. This process is also more efficient compared to the more expensive and complex DC step-up/step-down systems. Therefore, AC is used for power transmission.
Related Articles
Understanding Coupled Inductors: Operations and Practical Applications
Efficient Paper Packaging Machine Innovations
Capacitive Voltage Divider : Prinple & Its Applications










