ESP32 vs ESP8266: Which One Should You Choose?
What is the difference between ESP32 and ESP8266? Should you use ESP32 or ESP8266 in your project? In this article, we will compare the ESP32 vs ESP8266 and cover the pros and cons of each board.
Ⅰ. What is ESP32 and its advantages and disadvantages.
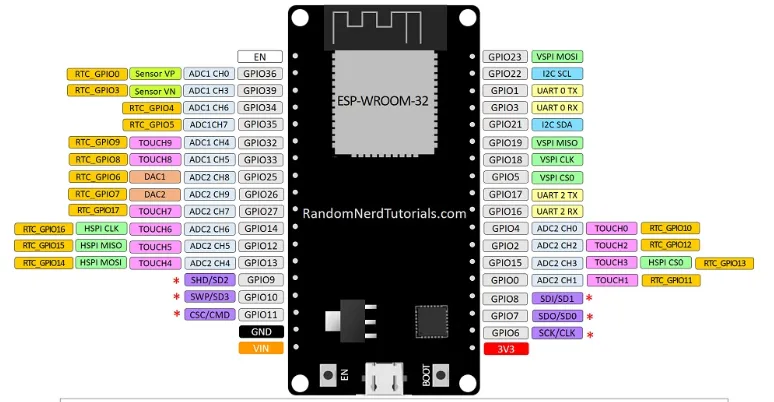
Figure1:ESP32 DEVKIT V1-DOIT
ESP32 is a series of low-cost chip microcontroller power systems. ESP32 is an advanced version of the ESP8266 series. The ESP32 series is created and developed by Espressif Systems. ESP32 has dual core and ultra-low power coprocessor. It was developed for the lack of security, which is implemented in the ESP8266.
ESP32:Advantage
ESP32 offers dual cores from 160MHZ to 240MHZ
Devices can be controlled and monitored via Wi-fi or Bluetooth at a fraction of the price.
ESP32 provides more GPIOs
ESP32 supports high speed of 150Mbps.
ESP32:Disadvantages
ESP32 is more expensive than ESP8266.
Ⅱ. What is ESP8266 and its advantages and disadvantages.
ESP8266 is a complete or standalone system-on-chip (SOC) circuit with Wifi module with IP/TCP protocol stack. The ESP8266 can be accessed via Wifi connection to any microcontroller.
One of the main functions of the ESP8266 is to host any application or offload all Wifi network functions.
It is extremely durable and performs consistently even in harsh industrial environments. This is simply because of its wide operating temperature range.
It also offers a power-efficient architecture and a 32-bit Tensilica processor.
ESP8266:Advantage
The ESP8266 module provides powerful onboard processing and storage capabilities, allowing it to be integrated with sensors and other applications.
Its chip integration is very high. Chip integration allows users to use very few external circuits.
ESP8266 is used together with APSD for Bluetooth and VoIP application coexistence interface. It also contains a self-calibrating radio frequency (RF), allowing it to operate under all operating conditions without the need for any RF parts.
ESP8266:Disadvantages
The ESP8266 does not have Bluetooth connectivity, while the ESP32 has Bluetooth connectivity.
There are very few GPIOs in ESP8266 compared to ESP32.
Ⅲ. Comparison table between ESP32 and ESP8266
|
Compare items |
ESP32 | ESP8266 | ||
| Clock frequency | 160 or 240MHz | 80MHzBluetooth support | ||
| Bluetooth support | × | |||
| Hall sensor | √ | × | ||
| Camera interface | × | × | ||
| Temperature Sensor | √ | × | ||
| touch sensor | 10 | × | ||
| safety | Secure Boot Flash Encryption, 1024-bit | × | ||
| Low power consumption | 10uA depth sensor | 20uA | ||
| coprocessor | ULP | × | ||
| GPSIO | 39 | 17 | ||
| Support decryption algorithm | RSARNGECCSHA-2AES | × | ||
| SPI | 4 | 2 | ||
| USB OTG | × | × | ||
| microcontroller | Single or dual core 32-bit LX6Xtensa | Single core 32-bit L106Xtensa | ||
| ROM | 448 KB | × | ||
| CAN | 2 | × | ||
| Ethernet | 10/100 Mbps | × | ||
| External SPIRAM | Maximum 16MB | Maximum 16MB |
Figure2:ESP32 vs ESP8266 table
Ⅳ. What is the difference between ESP8266 and ESP32?

Figure3:ESP32 vs ESP8266
01 .ESP8266
ESP8266 is a Wi-fi SoC that has all the important components that users need to use Wi-fi devices. The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi enabled microchip that can add wireless connectivity to any microcontroller.
ESP8266 is an integrated circuit with 16 GPIO pins and different peripherals such as serial peripheral interface, IC protocol, analog-to-digital converter.
ESP8266 does not have Ethernet and touch sensor. It has no remote control access and lacks security. The ESP8266 has no encryption or temperature sensor.
02ESP32
ESP32 is an upgraded version of ESP8266, it has 34 GPIO pins and comes with Xtensa dual-core processor 160MHZ.
The ESP32 has a 32-bit processor with an ultra-low-power coprocessor and multiple input/output connectors, including digital-to-analog converters. ESP32 provides a secure platform for the Internet of Things.
ESP32 provides remote control access and temperature sensor. ESP32 gives you the security of secure boot flash encryption 1024-bit OTP via PWM (soft) 16. ESP32 has ten touch sensors.
Ⅴ. ESP32 or ESP8266?

Figure4:ESP32 vs ESP8266
01ESP32 has one more CPU core than ESP8266, faster Wi-Fi, more GPIOs and support for Bluetooth 4.2 and Bluetooth Low Energy.
02ESP32 has a touch-sensitive pin that can be used to wake the ESP32 from deep sleep, a built-in Hall effect sensor, and a built-in temperature sensor (the latest version of the ESP32 no longer has a built-in temperature sensor).
The 03ESP8266 is a cheaper option suitable for simple projects.
For comparison, here is the pinout diagram for the ESP8266 ESP-12E NodeMCU kit.
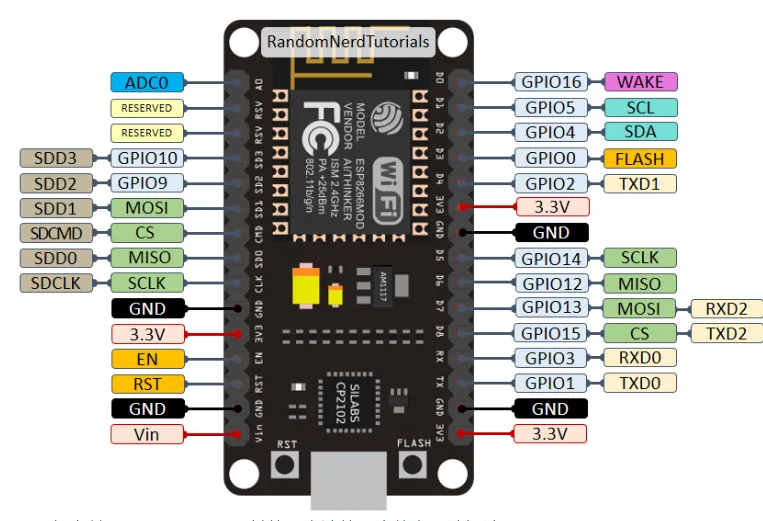
Figure5: ESP8266 GPIO
Ⅵ: Comparison of the internal structures of ESP32 and ESP8266
6.1. Core System: ESP32 and ESP8266
ESP32 and ESP8266:Same point
Cache: cache memory, also called cache
SRAM: static random access memory
JTAG: International standard test protocol (used for simulation and debugging, JTAG technology is an embedded debugging technology)
ROM: read-only memory, not lost when power is lost
ESP32 and ESP8266:Difference
ESP32-C2:
RISC-V32-bit Microprocessor: RISC-V 32-bit single-core processor, clocked up to 120MHz
ESP8266:
RTC SRAM: Real-time clock static random access memory
Tensilica L106 32 bit core processor: Tensilica L106 32 core processor, clocked at up to 160MHz
ESP32-C3:
RTC SRAM: Real-time clock static random access memory
RISC-V32-bit Microprocessor: RISC-V 32-bit single-core processor, clocked up to 160MHz
6.2. Wi-Fi radio frequency and baseband: ESP32 and ESP8266
ESP32 and ESP8266:Same point
2.4 GHz Receiver: 2.4 GHz receiver
2.4 GHz Transmitter: 2.4 GHz transmitter
WPA/WPA2: A new encryption method based on WPA
ESP32 and ESP8266:Difference
ESP32-C2/C3:
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi; 20Mhz and 40Mhz
Bluetooth LE v5.0
RF Synthesizer: Radio frequency synthesizer
2.4 GHz Balun + Switch: 2.4 GHz transformer and switch
ESP8266:
2.4GHz Wi-Fi; 20Mhz
WiFi up to 75 Mbps
6.3. Peripherals: ESP32 and ESP8266
ESP32 and ESP8266:Same point
GPIO: ordinary pin
RTC GPIO: RTC pin (low power consumption, controlled by the RTC subsystem of ESP32)
UART: serial communication
I2C: bus interface
SPI: serial communication bus
LED PWM: pulse width modulation dimming
General-purpose/System Timer: General-purpose/System Timer
RTC Watchdog Timer: Real-time clock watchdog timer, abbreviated as RWDT
Temperature Sensor: Temperature sensor
DIG ADC Controller: SAR analog-to-digital converter
GDMA: General DMA controller (for high-speed data transfer)
ESP32 and ESP8266:Difference
ESP32-C2:
Brownout: power outage detector
SiP Flash: Multimedia Communication Protocol
eFuse Controller: eFuse hot-swappable controller
ESP8266:
I2S: Audio input/output interface, supports linked list DMA
IR: IR infrared remote control interface
SDIO: Slave SDIO interface
ESP32-C3:
I2S: Audio input/output interface
RMT: Infrared transceiver
TWAI: TWAI controller
LCD interface: LCD interface
Pulse Counter: Pulse counter
Camera interface: camera interface
uSB Serial/JTAG: USB serial/JTAG controller
6.4. Real-time clock (RTC): ESP32 and ESP8266
ESP32 and ESP8266:Same point
ESP32-C2/C3
PMU: Power Management Unit, a microcontroller that controls the power function of a digital platform (the function of the on-chip PWU is to cut off the power to unnecessary parts)
ESP32 and ESP8266:Difference
ESP32-C3
RTCMemory: stores real-time data
Ⅶ. Application scenarios of ESP32 and ESP8266
Understanding how IoT modules are being used helps us identify areas where their true potential can be extracted. This module can play a better role in the following areas:
Use WiFi to triangulate a location.
Automated point of sale for various stores and workshops.
Industrial safety in the domestic and commercial sectors.
Wirelessly monitor CCTV cameras and sensors, providing data.
The field of robotics for academic and professional purposes.
Ⅷ. Summary: ESP32 and ESP8266
We know that both ESP32 and ESP8266 are very complete tool kits. When considering different factors, different modules need to be selected. When considering equipment cost, it may be more appropriate to choose ESP8266; when a larger number of GPIOs are required, ESP32 is more appropriate. Therefore, the specific choice of ESP32 and ESP8266 can only be made based on your actual application.










